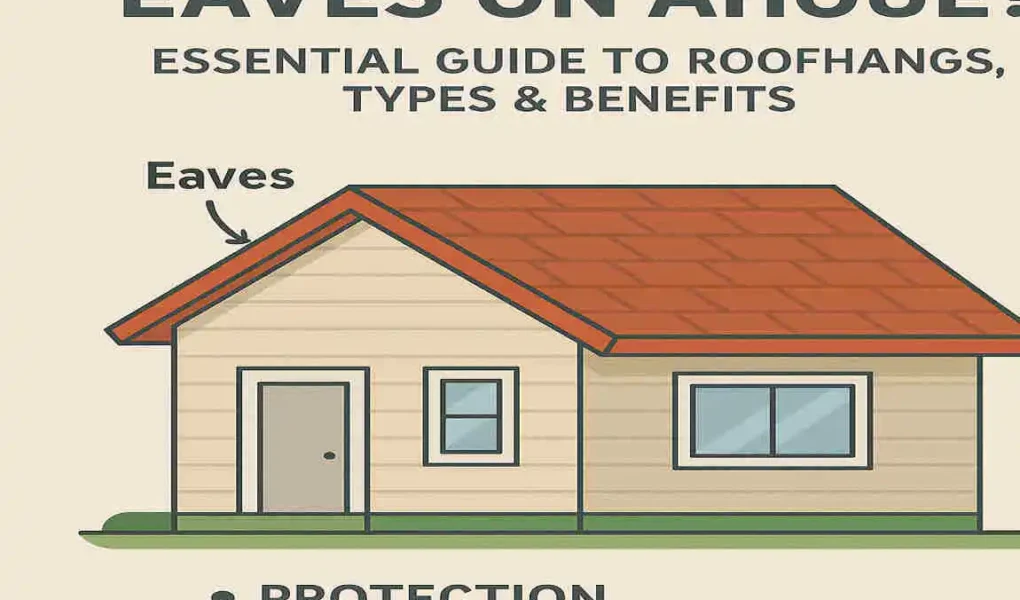
When it comes to maintaining and designing a home, the roof often takes center stage. But have you ever stopped to think about the eaves of your house? These seemingly small architectural features play a massive role in protecting your home from the elements while also boosting its overall aesthetic appeal.
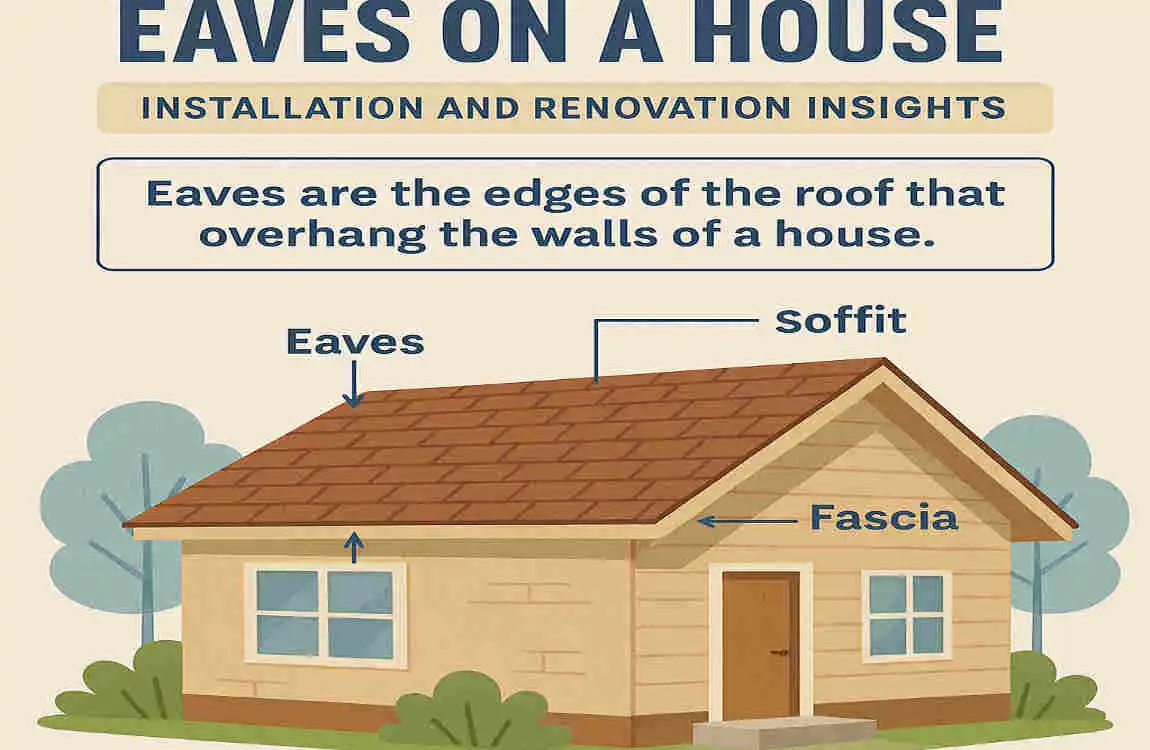
In simple terms, eaves are the lower edges of the roof that extend beyond the walls of a house. While they might seem like minor details, their functionality and design are crucial to the structural integrity and visual appeal of your home.
What Are Eaves on a House?
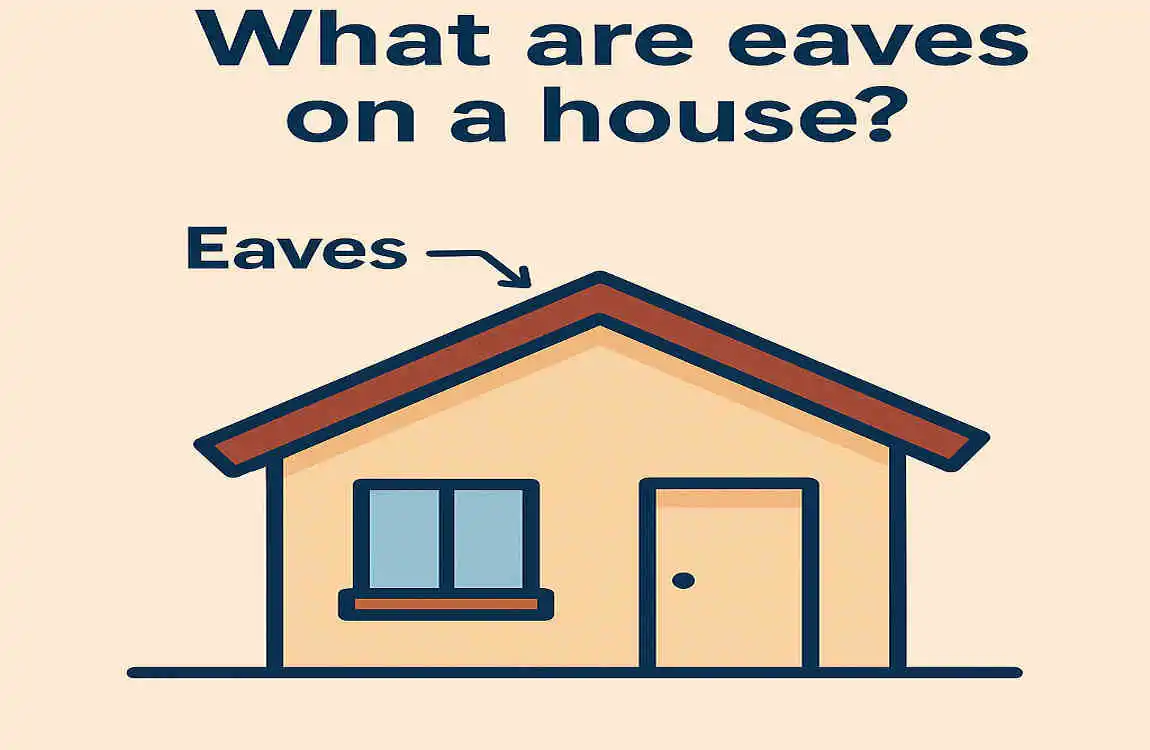
Definition of Eaves
Eaves are the lower portion of a roof that extends beyond the exterior walls of a house. They’re designed to create a protective overhang, shielding the house’s walls and foundation from rain, snow, and sunlight.
But eaves are more than just an overhang. They include key components that work together to provide both functionality and aesthetic value.
Components of Eaves
- Overhang: The portion of the roof that physically extends beyond the walls.
- Soffit: The underside of the eaves, usually covered with panels for a clean finish.
- Fascia Board: The vertical edge of the eaves, where gutters are often attached.
Eaves vs. Related Terms
It’s easy to confuse eaves with related roofing terms, such as soffits and fascia. Here’s a quick breakdown:
TermDefinition
Eaves: The entire overhanging section of the roof, including the soffit and fascia.
Soffit: The underside of the eaves, often ventilated for airflow.
Fascia: The vertical board covering the edge of the roof, supporting gutters and protecting the roofline.
The Importance of Eaves
Eaves are essential for:
- Weather protection: They direct water and snow away from the home’s walls and foundation.
- Ventilation: Soffits allow for airflow, preventing moisture buildup in the attic.
- Aesthetics: They add character and visual interest to a house.
Anatomy and Structure of Roof Eaves
To better understand eaves, let’s break down their structure and materials.
How Eaves Are Constructed
Eaves are built as part of the roof’s framing. The rafters or trusses of the roof are extended beyond the walls to create the overhang. Here’s a simplified process:
- The rafters form the roof’s skeleton and dictate the length of the overhang.
- Fascia boards are installed at the edge to cover the rafter ends and support gutters.
- Soffits are added beneath the overhang for a polished look and ventilation.
Materials Used in Eaves
The materials used in eaves depend on their location and purpose. Common options include:
- Wood: Traditional and versatile, but requires regular maintenance.
- Aluminum: Lightweight, durable, and resistant to rust.
- Vinyl: Low-maintenance and cost-effective, often used for soffits.
Architectural Significance
Eaves aren’t just functional—they’re also a key design element. From the wide overhangs of Craftsman-style homes to the sleek, minimal eaves of modern architecture, they can significantly influence a home’s appearance.
Types of Roof Eaves
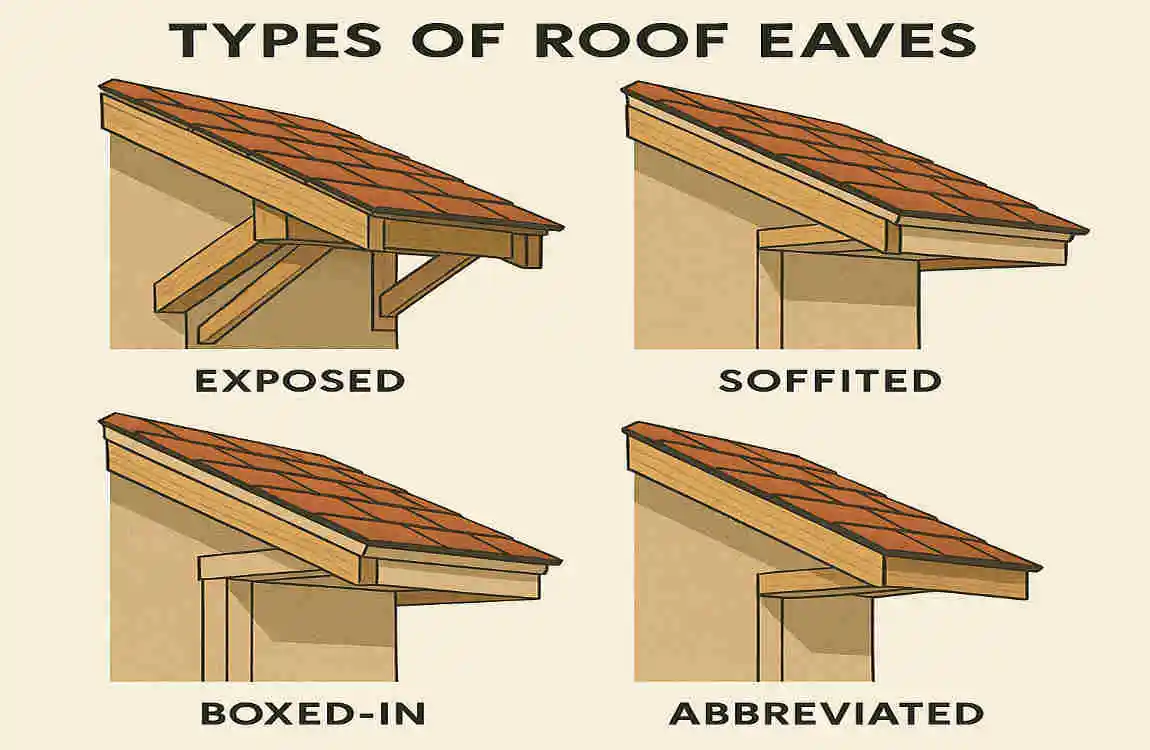
Eaves come in various styles, each with its own set of pros and cons. Let’s explore the most common types.
Open Eaves
Open eaves expose the ends of the rafters, creating a rustic and traditional look.
- Benefits: Excellent ventilation, adds character to the home.
- Drawbacks: Requires more maintenance and may attract pests.
Closed Eaves
Closed eaves are covered beneath soffits, creating a clean, finished appearance.
- Benefits: Protects against weather and pests.
- Drawbacks: Reduced ventilation compared to open eaves.
Boxed Eaves
Boxed eaves are fully enclosed, with both soffits and fascia boards for maximum durability.
- Benefits: Ideal for storm-prone areas, highly protective.
- Drawbacks: Can be more expensive to install.
Overhanging Eaves
Overhanging eaves extend further than standard eaves, providing additional protection from the sun and rain.
- Benefits: Great for hot or rainy climates.
- Drawbacks: May require extra structural support.
Abbreviated Eaves
Abbreviated eaves are minimal or nonexistent, often seen in modern architectural designs.
- Benefits: Sleek, contemporary look.
- Drawbacks: Less protection from the elements.
Benefits of Eaves on a House
Eaves do much more than look good. Here’s why they’re a vital part of any modern house:
Weather Protection
Eaves shield your home from rain, snow, and sunlight. By directing water away from the walls and foundation, they help prevent:
- Water damage to the siding.
- Foundation issues caused by pooling water.
- Mold and mildew growth.
Ventilation
Properly ventilated eaves (with soffit vents) allow airflow into the attic, preventing:
- Moisture buildup.
- Condensation that can damage insulation.
- Overheating during the summer.
Energy Efficiency
Eaves can shade windows and walls, reducing summer heat gain. This can lower cooling costs and create a more comfortable indoor environment.
Pest Control
Closed or boxed eaves can prevent birds, rodents, and insects from nesting in your roof. Regular maintenance further reduces the risk of infestations.
Enhanced Aesthetics
Eaves are a defining feature of many architectural styles. Whether it’s the deep overhangs of a bungalow or the minimal eaves of a modern home, they add character and visual appeal.
Common Problems and Maintenance Tips for Eaves
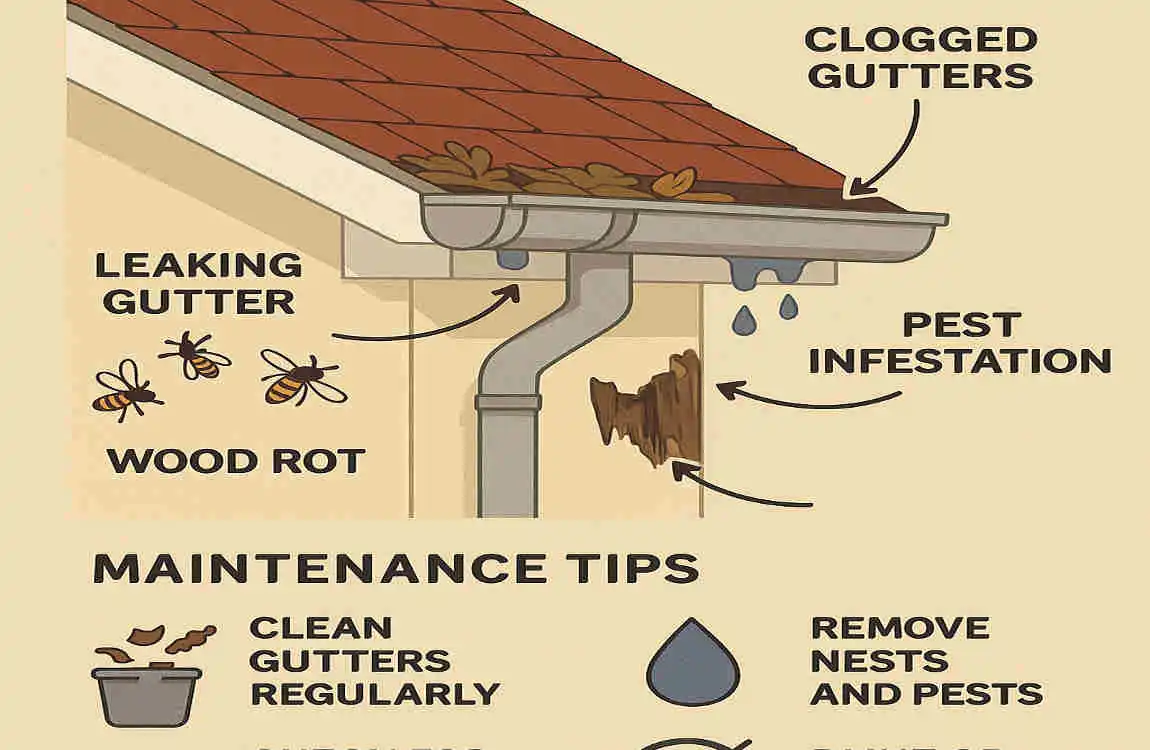
Like any part of your home, eaves require regular care. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
Water Damage
Clogged gutters or poor drainage can cause water to pool around the eaves, leading to:
- Rotting wood.
- Peeling paint.
- Structural damage.
Pest Infestations
Birds, bees, and other pests often find eaves an inviting place to nest.
Wear and Tear
Over time, eaves can show signs of aging, such as:
- Cracked or rotting fascia boards.
- Loose gutters.
Solution: Conduct yearly inspections and address issues promptly.
How to Choose the Right Eave Style for Your Home
Selecting the perfect eave style depends on several factors:
Climate Considerations
- In rainy climates, overhanging or boxed eaves offer better protection.
- Hot climates: Wide eaves provide shade and reduce heat gain.
Architectural Style
Match the eave style to your home’s design. For example:
- Craftsman homes: Open eaves.
- Modern homes: Abbreviated eaves.
Budget
While open eaves are cost-effective, boxed eaves offer more durability and long-term benefits.
Installation and Renovation Insights
Installation Process
Eaves are installed during roof construction. Key steps include:
- Extending the rafters.
- Installing fascia boards and soffits.
- Adding gutters and flashing for water management.
Renovation Tips
If your eaves are damaged, consider:
- Replace rotted wood with durable materials, such as aluminum.
- Adding soffits to improve ventilation.
- Upgrading gutters for better drainage.
FAQs About Eaves on a House
What’s the difference between eaves and soffits?
Eaves refer to the entire overhang, while soffits are the underside panels of the eaves.
Can eaves prevent foundation problems?
Yes! By directing water away from the house, eaves help protect the foundation from water damage.
How often should eaves be inspected?
At least once a year, and after significant storms.
Are boxed eaves better than open eaves?
Boxed eaves provide more protection and durability, but open eaves offer better ventilation and a rustic look.