Humidity plays a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable and healthy living environment. Many homeowners often wonder, “Why is it more humid in my house than outside?” This is a common question, as indoor humidity levels can significantly impact air quality, personal comfort, and even the structural integrity of your home.
Understanding Humidity and Its Effects
Before diving into the solutions, let’s first understand what humidity is and how it affects your home. Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor present in the air. There are two types of humidity: absolute humidity and relative humidity. Absolute humidity measures the actual amount of water vapor in the air. In contrast, relative humidity is the percentage of water vapor in the air compared to the maximum amount of water vapor it can hold at a given temperature.
High indoor humidity can lead to various problems, such as:
- Mold and mildew growth
- Dust mite infestations
- Respiratory issues and allergies
- Damage to wooden furniture and structures
- Musty odors and discomfort
Even when outdoor conditions are not particularly humid, indoor humidity levels can still rise due to various factors within your home.
Reasons Why It’s More Humid in Your House Than Outside
Poor Ventilation and Air Circulation
One of the primary reasons for high indoor humidity is inadequate ventilation and air circulation. When moist air becomes trapped inside your home, it can quickly lead to a buildup of moisture. This is especially common in areas with limited airflow, such as basements, attics, and bathrooms.
Water Sources Inside the House
Everyday activities, such as cooking, bathing, and cleaning, introduce moisture into the air. If your home lacks proper ventilation, excess moisture can accumulate, resulting in higher humidity levels. Indoor plants, while beneficial for air quality, can also contribute to increased humidity if not appropriately managed.
Building Materials Trapping Moisture
Certain building materials, such as concrete and wood, can absorb and retain moisture. If these materials are not adequately sealed or treated, they can release moisture back into the air, causing a rise in humidity levels.
Leaks and Moisture Infiltration
Leaks in your home’s structure, such as those in the roof, plumbing, or windows, can allow moisture to enter and contribute to high indoor humidity. It’s essential to identify and fix any leaks promptly to prevent further moisture buildup.
Insufficient Use or Absence of Dehumidifiers or Ventilation Systems
If your home lacks proper dehumidification or ventilation systems, it can be challenging to effectively control indoor humidity levels. Dehumidifiers help remove excess moisture from the air, while ventilation systems promote air circulation and prevent stagnant, humid air from accumulating.
Climate and Seasonal Impacts
Depending on your location, climate, and seasonal changes, indoor humidity levels can be significantly influenced. During the summer months or rainy seasons, outdoor humidity tends to be higher, which can lead to increased indoor humidity if not appropriately managed.
How to Measure and Monitor Indoor Humidity
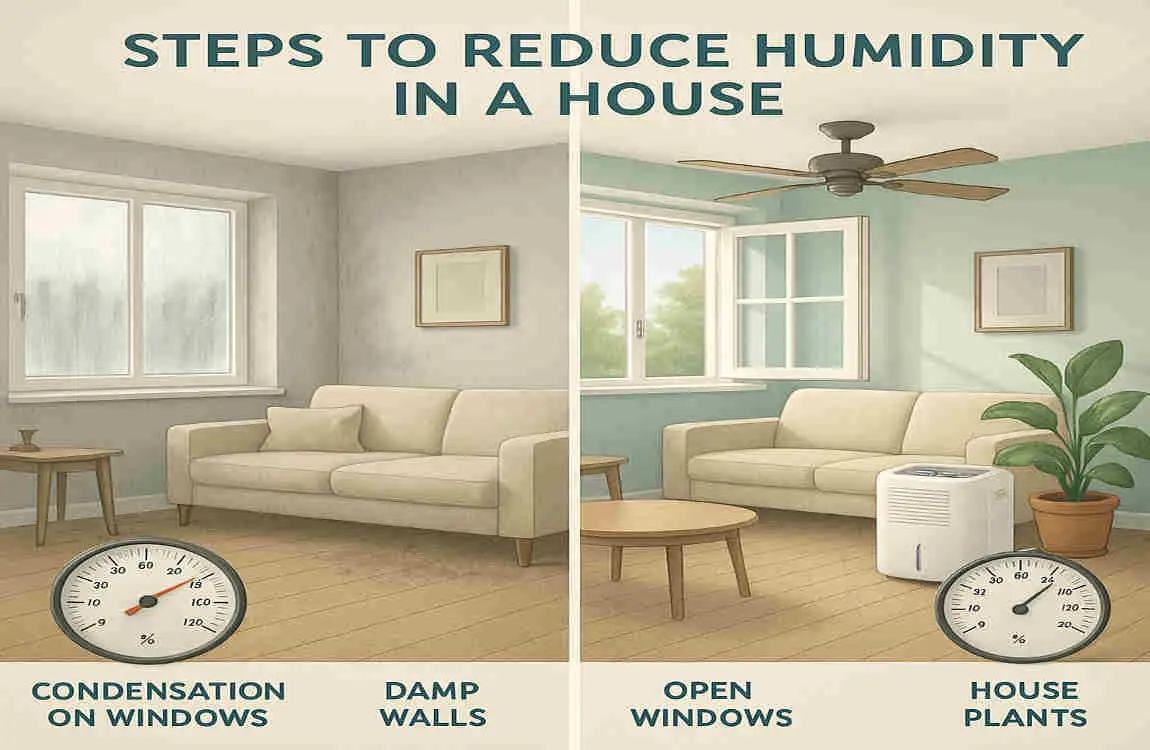
To effectively control indoor humidity, it’s crucial to measure and monitor it regularly. Here are some tools and tips to help you keep track of your clean home‘s humidity levels:
- Hygrometers measure the relative humidity in a given space. You can purchase standalone hygrometers or opt for smart home sensors that integrate with your home automation system.
- Ideal Indoor Humidity Range: The ideal relative humidity range for indoor environments is between 30% and 50%. Keeping your home within this range helps maintain comfort, prevent mold growth, and protect your belongings.
- Regular Monitoring: Make it a habit to check your home’s humidity levels regularly, especially during seasons when humidity tends to be higher. This enables you to identify any issues promptly and take the necessary action.
Practical Steps to Reduce Humidity in Your House Effectively
Now that you understand the causes and effects of high indoor humidity, let’s explore practical solutions to effectively reduce it.
Improving Ventilation
- Exhaust Fans: Install exhaust fans in areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms and kitchens. Run these fans during and after activities that generate steam or moisture, such as showering or cooking.
- Opening Windows Strategically: When the weather permits, open windows on opposite sides of your home to create a cross breeze. This helps promote air circulation and allows moist air to escape.
- Ventilation Systems: Consider installing a whole-house ventilation system, such as a heat recovery ventilator (HRV) or energy recovery ventilator (ERV). These systems exchange stale, humid indoor air with fresh, conditioned outdoor air, maintaining a balanced humidity level.
Using Dehumidifiers
- Types of Dehumidifiers: There are two main types of dehumidifiers: portable and whole-house units. Portable dehumidifiers are suitable for smaller spaces or specific rooms, while whole-house dehumidifiers are integrated into your HVAC system and work to control humidity throughout your entire home.
- Placement: Position portable dehumidifiers in the most humid areas of your home, such as basements or closed-off rooms. Ensure the unit has adequate space around it for proper air circulation.
- Maintenance: Regularly clean or replace the air filters in your dehumidifier to maintain its efficiency. Empty the water collection tank as needed, or set up a drainage hose for continuous operation.
Fixing Leaks and Waterproofing
- Identify and Repair Leaks: Inspect your home for any visible leaks in the roof, plumbing, or windows. Repair these leaks promptly to prevent moisture from entering your home.
- Waterproofing: In areas prone to moisture infiltration, such as basements or crawl spaces, consider waterproofing solutions. This may include applying sealants, installing a vapor barrier, or using a French drain system to redirect water away from your home’s foundation.
Managing Household Moisture Sources
- Drying Clothes Indoors: Avoid hanging wet clothes indoors to dry, as this can significantly increase humidity levels. Use a clothes dryer or hang clothes outside when possible.
- Covering Pots and Pans: When cooking, use lids on pots and pans to minimize the amount of steam released into the air.
- Houseplant Care: While plants can improve air quality, overwatering them can actually contribute to higher humidity levels. Water plants only when necessary and ensure proper drainage to prevent excess moisture.
Upgrading HVAC Systems
If your home’s HVAC system lacks humidity control features, consider upgrading to a system with built-in dehumidification capabilities. This can help maintain a consistent humidity level throughout your home, improving comfort and air quality.
Using Moisture-Absorbing Materials
- Silica Gel: Place packets of silica gel in areas prone to moisture, such as closets or drawers, to absorb excess humidity.
- Desiccants: Use desiccant materials, like charcoal briquettes or calcium chloride, to absorb moisture in small, enclosed spaces.
Seasonal Adjustments and Routine Maintenance
As seasons change, adjust your humidity control strategies accordingly. During summer months or rainy seasons, you may need to use dehumidifiers more frequently or increase ventilation. Regularly maintain your HVAC system, dehumidifiers, and ventilation equipment to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
DIY Solutions vs Professional Help
While many humidity control solutions can be implemented through DIY methods, there are situations where professional help is necessary. If you have persistent humidity issues, suspect mold growth, or have complex HVAC or structural concerns, consult with a qualified professional to assess your home and provide tailored solutions.
Benefits of Controlling Indoor Humidity
By effectively reducing humidity in your indoor humidty house, you can enjoy numerous benefits, such as:
- Improved Health: Lowering humidity levels can reduce allergens such as dust mites and mold spores, providing relief for individuals with allergies or respiratory issues.
- Home Preservation: Controlling humidity helps prevent damage to your home’s structure, furniture, and belongings caused by excess moisture.
- Enhanced Comfort: A balanced humidity level creates a more comfortable living environment, preventing that sticky, muggy feeling often associated with high humidity.
- Better Air Quality: By reducing mold growth and other humidity-related issues, you can improve the overall air quality in your home.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Humidity Control
When working to reduce indoor humidity, be mindful of these common mistakes:
- Ignoring Small Leaks: Even small leaks can contribute to significant moisture buildup over time. Address any leaks promptly, no matter how minor they may seem.
- Overusing Humidifiers: While humidifiers can be beneficial during dry seasons, overusing them can lead to excessive humidity. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and closely monitor humidity levels.
- Temporary Fixes: Avoid relying solely on temporary solutions, such as running a dehumidifier without addressing underlying issues like poor ventilation or leaks. Tackle the root causes for long-term humidity control.
- Inappropriate Tools or Settings: Ensure you use the right tools and settings for your specific home environment. Using a dehumidifier with a capacity too small for your space or setting it to an incorrect humidity level can hinder its effectiveness.