Windows are one of the most critical features of any house design. They don’t just provide natural light, ventilation, and aesthetic appeal, but they also play a crucial role in defining the functionality and visual harmony of a home. Whether you’re a budding architect, an interior designer, or a DIY enthusiast, understanding how to draw a window for a house is an essential skill.
Understanding Windows in House Plans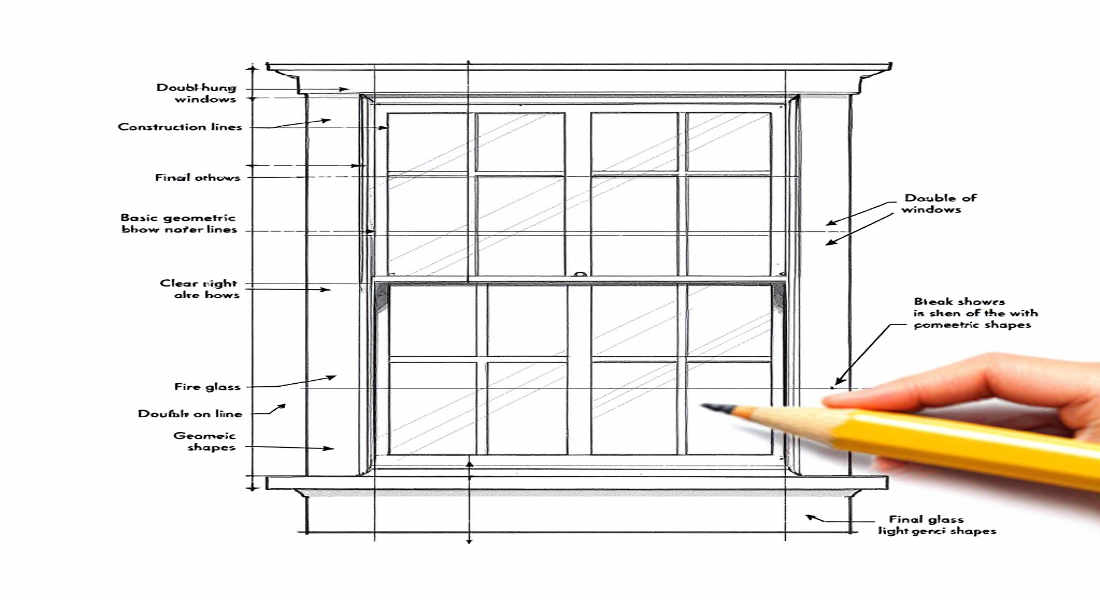
Before you start drawing, it’s important to understand the different types of windows and their unique applications. Each window type has its own design, function, and symbolism in architectural plans. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
Common Types of House Windows
Single-Hung Windows
These windows feature two sashes, but only the bottom sash moves vertically while the top sash remains fixed. They are simple, cost-effective, and ideal for traditional home designs.
Double-Hung Windows
Unlike single-hung windows, both the top and bottom sashes of double-hung windows can move. They offer greater ventilation options and are popular in modern homes.
Casement Windows
Casement windows are hinged on the side and open outward like a door. They are great for maximizing ventilation and work well in areas where space outside the window is not a constraint.
Sliding Windows
Sliding windows feature sashes that move horizontally. They are perfect for wide wall spaces and offer an unobstructed view of the outdoors.
Fixed Windows
As the name suggests, fixed windows do not open. Their purpose is purely aesthetic or to allow light into spaces where ventilation isn’t needed, such as staircases or high ceilings.
Why Choosing the Right Window Type Matters
Each window type affects how you draw and represent it on a house plan. For example:
- Single- and double-hung windows have distinct sash lines that need to be drawn.
- Casement windows require arcs or arrows to indicate their swing direction.
- Fixed windows are simpler to draw as they lack movable parts.
When selecting a window, consider its functionality, style, and how it fits into the overall design of the house. Accurate representation of your plans ensures that the construction team understands your vision.
Tools and Materials Needed for Drawing Windows
To create precise and professional-looking window drawings, you need the right tools. Here’s a list of essential materials:
You may also read (windows to the side of your house).
Traditional Tools
- Ruler: A good-quality ruler ensures straight, accurate lines.
- Scale Ruler: This helps you draw to scale, which is crucial for architectural plans.
- Pencil and Eraser: Pencils allow flexibility for adjustments, and erasers help keep your plans neat.
- Graph Paper: Using graph paper makes it easier to maintain proportions and align your drawings.
Digital Tools
- AutoCAD: A professional tool for 2D and 3D architectural designs.
- Revit: Ideal for creating detailed floor plans and 3D models.
- SketchUp: A beginner-friendly tool for quick and easy designs.
- Coohom: Especially designed for interior and architectural planning.
Why Accuracy Matters
Using the right tools ensures precision in your drawings. For instance, a scale ruler helps you maintain proportionality, while digital tools allow for easy edits and detailed renderings. Whether you’re drawing by hand or using software, accuracy is key to a functional and aesthetically pleasing design.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Draw a Window for a House
Now that you understand window types and have the right tools, it’s time to dive into the actual drawing process. Follow these steps to create a professional window design for your house plan:
Determine Window Location
- Identify where the window will be placed on the house plan.
- Consider factors like room orientation, natural light needs, views, and wall thickness.
- Place windows strategically to maximize ventilation and sunlight.
Measure the Window Opening
- Measure the width and height of the window opening. Use a scale ruler if working on paper.
- Ensure the dimensions comply with local building codes for safety and functionality.
Draw the Window Opening on the Plan
- Using graph paper or software, draw a rectangular box to represent the window opening.
- Align the window with the wall to avoid misplacement.
You may also read (floor damage on your home).
Add the Window Frame
- Inside the window opening, draw an inner rectangle to represent the frame.
- Use proportional thickness to differentiate the frame from the opening.
Draw the Window Sashes and Glass
- For movable windows, draw the sashes and indicate their position.
- Add mullions or muntins (grids) if applicable to the design.
Indicate Window Operation and Orientation
- Add arcs or arrows to show how the window opens, whether it swings outward (casement) or slides horizontally.
Add Details
- Incorporate hardware like handles, locks, and trims to make the drawing more realistic.
Label the Window
- Clearly label the dimensions and window type (e.g., “4 ’ x 3’ Double-Hung Window”).
Final Review and Adjustments
- Double-check alignment with walls and other architectural elements.
- Ensure the drawing is proportional and adheres to the scale.
Tips and Best Practices for Drawing Windows
To make your window drawings stand out, follow these tips:
- Use a Grid System: This ensures consistency and precision.
- Match Style with Design: Select window styles that align with the overall house theme.
- Keep Lines Clean: Use sharp pencils or fine digital tools for neat, professional lines.
- Add Shading and Lighting: Use shading to show depth and light direction for a realistic effect.
- Follow Standards: Use standardized symbols to make your drawings universally understandable.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Drawing Windows
Even experienced designers can make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
- Incorrect Window Size: Always double-check your measurements to prevent disproportionate designs.
- Misrepresenting Window Shape: Ensure the window shape matches its intended type (e.g., rectangular for sliding windows).
- Overlooking Frame Details: Don’t forget to include frame thickness and hardware.
- Not Indicating Operation: Use arrows or arcs to show how the window opens.
- Ignoring Building Codes: Research and adhere to local regulations for window sizes and placements.
Using Software to Draw Windows on House Plans
Digital tools have revolutionized architectural design. Here’s a quick guide to using software for Windows drawings:
Popular Software Options
- AutoCAD: Offers precision and advanced features for architects.
- Revit: Provides detailed 3D modeling and professional floor plans.
- SketchUp: Perfect for beginners with its intuitive interface.
- Coohom: Tailored to create window designs for interior and architectural plans.
Benefits of Digital Drawing
- Accuracy: Measurements are precise and easy to adjust.
- Visualization: Create 3D models to see how windows look in real time.
- Efficiency: Make edits quickly without starting from scratch
You may also read (window in a house called).




