Understanding how our house plugs are wired? A simple home guide is essential for homeowners who want to stay safe, save money, or even take on DIY electrical projects.
Why Understand House Plug Wiring?
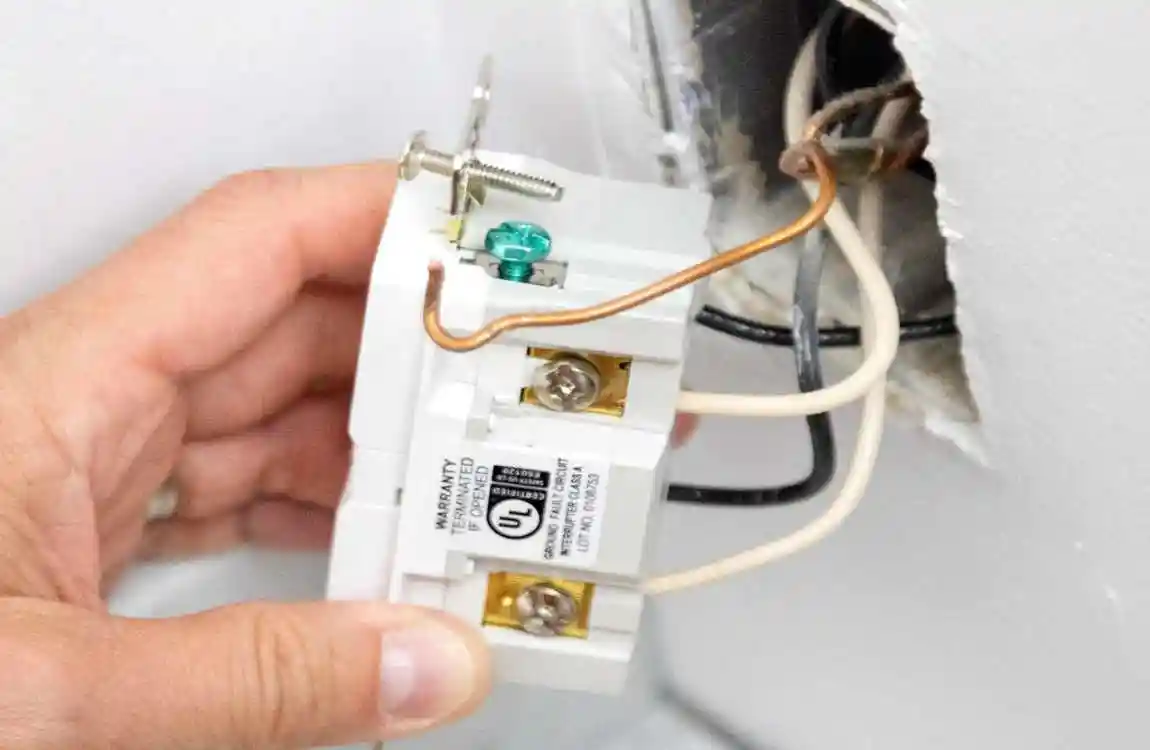

Before grabbing your screwdriver, it’s important to know why understanding plug wiring matters so much.
Safety Comes First
Poorly wired plugs can cause electric shocks, short circuits, or even fires. In fact, faulty electrical devices account for a significant percentage of home fires each year. Knowing the basics of wiring can help you spot problems early and avoid accidents.
Cost Savings and Convenience
Learning to wire plugs yourself saves you money on electrician fees for small repairs or installations. It also empowers you to troubleshoot issues quickly without waiting for professional help.
Regional Standards Matter
Different countries have their own wiring standards to ensure safety and consistency.
- UK: Uses BS 1363 standard with 3-pin plugs that include built-in fuses.
- US: Follows NEMA standards with polarized or grounded outlets.
Each has its own wiring colors, plug design, and safety rules, which we’ll explore in detail.
Types of House Plugs and Outlets
House plugs vary widely depending on where you live. Let’s break down the most common types you’ll encounter.
UK Plugs (BS 1363)
The UK plug is famous for its three rectangular pins:
- Live (brown wire): Carries current to the appliance.
- Neutral (blue wire): Returns current to the supply.
- Earth (green/yellow wire): Safety ground wire.
Each plug also contains a fuse to protect your appliances from electrical surges.
US Outlets (NEMA Standards)
In the US, you’ll find mostly:
- 2-prong outlets: Hot and neutral wires, ungrounded.
- 3-prong outlets: Add a ground wire for safety.
- GFCI outlets: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters, required in wet areas like bathrooms.
Other Regional Types
Different regions follow different standards, as shown in the table below:
Region Pins Fuse? Ground? Common Voltage
UK 3 Yes Yes 230V
US 2-3 No Optional 120V
EU 2-3 No Yes 230V
Understanding the type of plug is your first step to wiring it correctly.
Wiring Colors and Standards

When wiring plugs, colors mean specific things — mixing them up can be dangerous. Here’s how to recognize and use wiring colors correctly.
UK Wiring Colors (Post-2004)
- Brown: Live wire
- Blue: Neutral wire
- Green/Yellow: Earth (ground) wire
Older UK wiring (pre-2004) used different colors (red for live, black for neutral), so always check if you’re working with older cables.
US Wiring Colors
- Black: Hot (live) wire
- White: Neutral wire
- Green or bare copper: Ground wire
Why Colors Matter
Terminals on plugs and outlets are clearly labeled as Live (L), Neutral (N), and Earth (E). Connecting the wrong wire to a terminal risks electric shock or appliance damage.
Tools Needed for Wiring
Before you start wiring, gather the right tools:
- Screwdriver set: Both flathead and Phillips.
- Wire strippers: To remove insulation cleanly.
- Voltage tester: To ensure power is off before you touch wires.
- Pliers: For twisting wires.
- Insulated gloves: For extra safety.
Step-by-Step: How to Wire a UK House Plug

Wiring a UK plug might seem tricky, but with some patience, you can do it safely.
Prepare the Cable
Carefully cut off the cable’s outer sheath without damaging the inner wires. Strip about 6mm of insulation from each wire to expose the copper strands.
Open the Plug
Unscrew the plug cover and open it to access the terminals.
Identify the Wires
Match the colors to terminals:
- Brown wire → Live terminal (marked L, near the fuse).
- Blue wire → Neutral terminal (marked N).
- Green/yellow wire → Earth terminal (top pin, marked E).
Secure the Wires
Twist the exposed strands to keep them neat. Insert each wire firmly into its terminal and tighten the screws clockwise until secure.
Check the Fuse
Make sure the fuse rating matches your appliance (typically between 3A and 13A).
Close and Test
Replace the plug cover, tighten screws, and give each wire a gentle tug to ensure it’s secure. Use a voltage tester or plug tester to verify correct wiring.
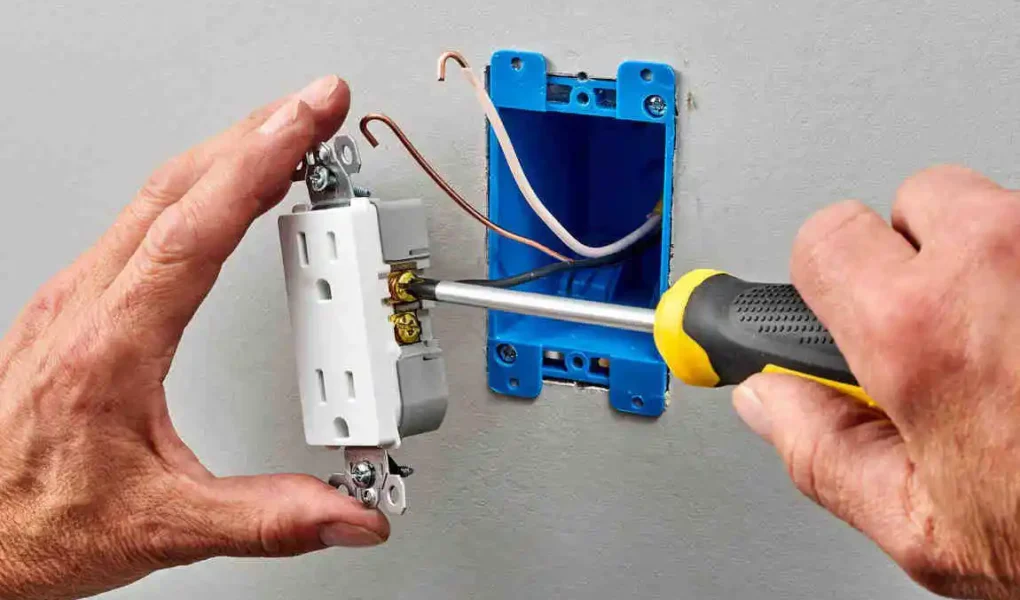
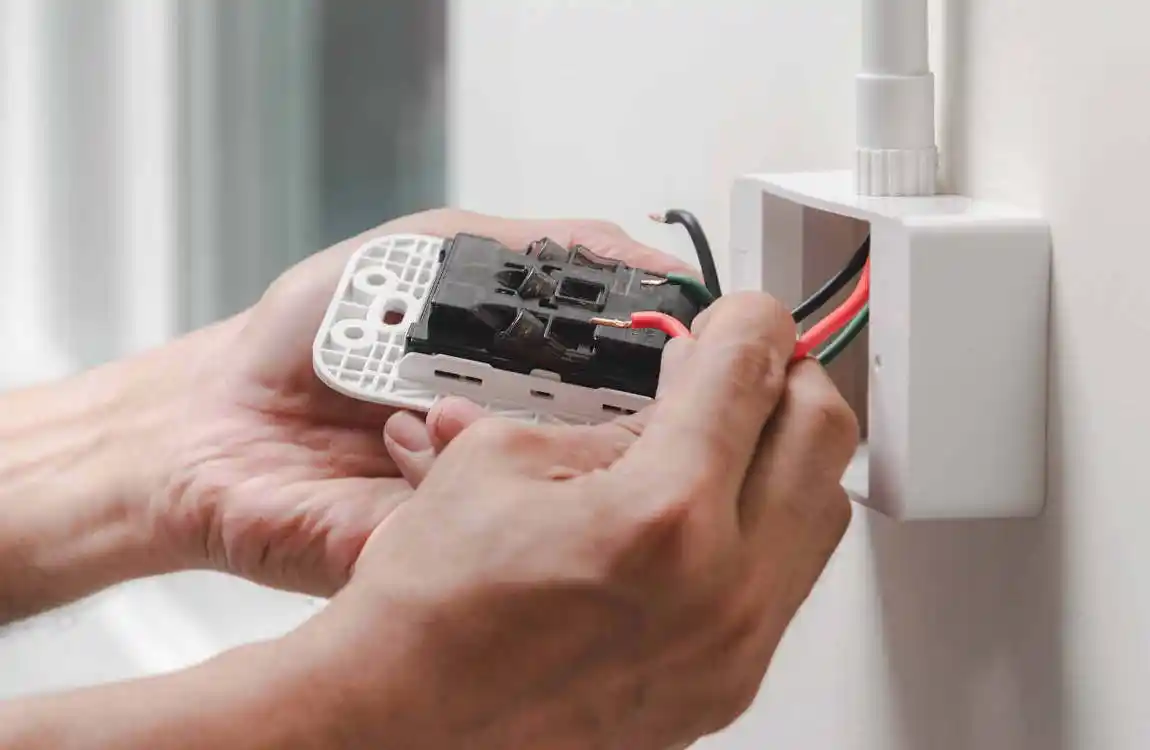
Step-by-Step: Wiring a US House Outlet
Wiring US outlets requires attention to detail and safety precautions.
Turn Off Power
Flip the circuit breaker to the off position and use a voltage tester to confirm that no electricity is flowing.
Remove the Cover Plate
Unscrew the outlet cover and loosen the outlet from the box.
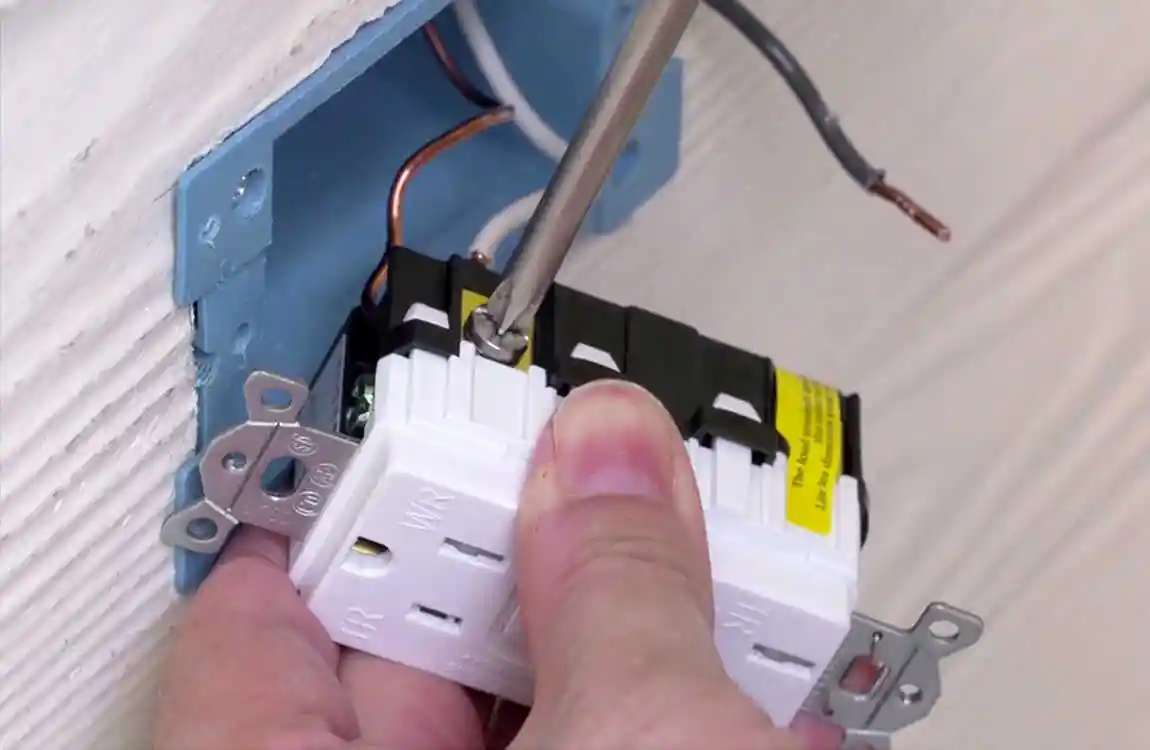
Connect the Wires
- Black wire to brass-colored terminal (hot/live).
- White wire to silver-colored terminal (neutral).
- Green or bare wire to green terminal (ground).
Pigtail Method
For multiple outlets on one circuit, use a short wire “pigtail” to connect several wires to a single terminal.
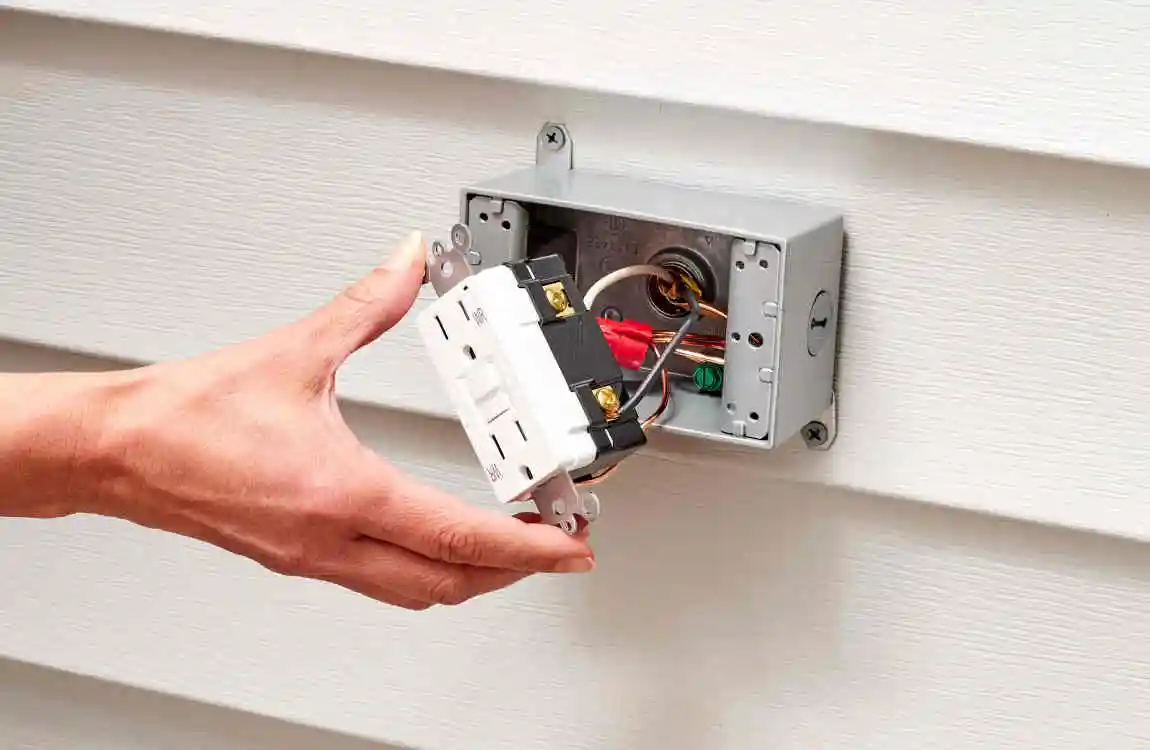
Wiring a GFCI Outlet
Connect the incoming power wires to the line terminals, and the downstream wires to the load terminals, to enable ground-fault protection.
Wire Color Terminal Purpose
Black Brass Hot/Live
White Silver Neutral
Green Green Ground
Diagrams and Visual Guides
Visual aids make wiring less intimidating. Here are some simple diagrams you can refer to:
UK Plug Internal Wiring
[Live Terminal (L)] — Brown wire
[Neutral Terminal (N)] — Blue wire
[Earth Terminal (E)] — Green/Yellow wire
US Outlet Wiring
[Brass Terminal] <– Black (Hot)
[Silver Terminal] <– White (Neutral)
[Green Terminal] <– Green (Ground)
Common Wiring Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced DIYers slip up. Here’s what to watch out for:
- Reversed Polarity: Connecting live and neutral wires backward can cause shocks.
- Loose Connections: Loose screws can cause arcing and fires.
- Wrong Fuse Rating: Using a fuse that’s too high risks damaging appliances.
- Ignoring Earth Wire: Skipping grounding wires increases the risk of shock.
MistakeRiskFix
Loose Screw Arcing/Fire : Tighten the screw clockwise
No Earth Wire Shock Hazard . Add grounding wire
Wrong Fuse Appliance Damage Use the correct fuse rating
Safety Tips and When to Call a Pro
Always De-Energize Circuits
Never work on live wires. Always switch off the power at the breaker and test.
Use GFCI Outlets in Wet Areas
Bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoors require GFCI protection to prevent shocks.
Know When to Hire an Electrician
If you’re rewiring walls, dealing with old or damaged wiring, or unsure of local codes, it’s safer to call a licensed pro.
Legal Considerations
Certain electrical work requires permits and inspections. Check your local regulations before starting.